Interview with Anurag Kamal, CEO & Co-Founder of ElectricFish #48
Smart energy storage and fast charging for communities
Hello Human,
It’s good to be back after three weeks! I got sick the other week but am back in action now.
Today, I’m excited to introduce you to Anurag Kamal, CEO & Co-Founder of ElectricFish! ElectricFish is an SF Bay Area-based startup on a mission to build resilient energy infrastructure for communities. They are developing a drop-in, integrated energy storage and fast EV charging solution.
➡️Follow Survivaltech.club on Twitter and Linkedin💚
🗞️Hardware x Deeptech x Climate News
These funding and other announcements recently caught my eye:
🔥Dandelion Energy, a US-based geothermal startup, raised a $70M Series B funding round.
🏗️Hyperion Robotics, a Finnish startup developing large-scale 3D printing with low-carbon concrete, raised €3M in seed funding.
🚛Volta Trucks, a Swedish electric truck manufacturer, closed a $60M extension to its Series C.
🐔Upside Foods, a US-based cultivated meat startup, got a greenlight from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its cultivated chicken in the pre-market consultation.
💰Energy Impact Partners launched a $485M Frontier fund that invests in early-stage deep tech climate startups.
💰Climate Adaptive Infrastructure raised over $1B for large-scale, low-carbon real asset investments in the clean energy, water, and urban infrastructure sector.
Which major news should I have included on this list? Message me here!
⚡New challenges of the grid
The electric grid experiences new challenges as more intermittent renewable energy generation is added, EV adoption accelerates, and extreme weather events become more frequent and intense.
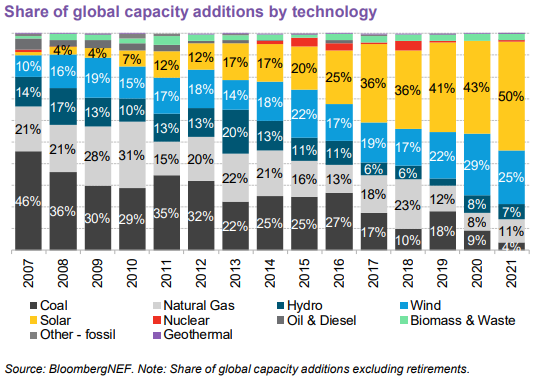
BloombergNEF reported that renewables accounted for 85% of the total increase in global power-generating capacity in 2021. The intermittent renewable energy sources, solar and wind, made up 50% and 25% of all the capacity additions, respectively. Consequently, the world’s energy storage installations are expected to grow by 15x between 2022 and 2030.
EVs are experiencing remarkable growth. In the US, the recently passed Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) is expected to accelerate EV sales such that over 50% of new car sales will be EVs in 2030. In some countries, EVs already make up a good chunk of car sales, reaching 24% of car sales in China and a staggering 84% in Norway.
EV adoption will likely strain the local grid by increasing electricity demand and peak loads.
The effects of the climate crisis are, unfortunately, already unfolding, and extreme weather events have become more frequent and intense. Hence, more localized backup energy storage has to be deployed to make the grid more resilient.
If you want to learn more about the electric grid, take a look at Survivaltech.club’s deep dive series on the electric grid (part 1 & part 2)!
💚ElectricFish’s solution
ElectricFish is a San Francisco Bay Area-based startup building resilient energy infrastructure for communities.
ElectricFish develops and deploys integrated energy storage and extreme-fast EV charging units. Their smart energy storage units store electricity when electricity is abundant and then power EVs with the stored electricity when needed.
🧠Wisdom from Anurag
How did you start work in climate? What’s the founding story of ElectricFish?
My first job was in truck manufacturing at Eicher Motors, a subsidiary of Volvo. During those two years, I transitioned from working with conventional transmission (internal combustion engines) to electric transportation as the company started to develop its first electric truck. At Eicher, I came to realize the important role electric vehicles can play in reducing emissions.
At the same time, Tesla was being built in the US, and I t became increasingly excited about the future of electric transportation. This excitement led me to want to learn more about EVs and pursue my Master’s in Mechanical Engineering at Michigan Technological University.
At Michigan Tech, I started reading about different technologies involved in EVs, such as inverters, motors, and batteries. Batteries caught my attention, and I eventually wrote my Master’s thesis on the mathematical modeling of aging in lithium-ion cells.
This unique insight, which later led to launching ElectricFish, developed organically over the years through researching in academia and working in the industry. After graduation, I joined BMW in Silicon Valley to work on i4 electric optimization systems and attended numerous industry and climate conferences. I understood there was a massive need for energy storage and EV charging infrastructure in the coming years and that integrating those two domains would make sense.
I pitched my idea of an integrated energy storage and EV charging service at a hackathon in SF in December 2019. Vince Wong and Nelio Batista, who later became my co-founders, wanted to work with me on this idea. After the hackathon, we continued working together and attended an accelerator at Stanford Graduate School of Business, where we met Folasade Ayoola, our 4th co-founder.
What is ElectricFish building? What are the benefits of your integrated solution?
We at ElectricFish are upgrading the grid infrastructure with our energy storage and fast EV charging unit. Our integrated solution can be deployed, for example, at gas stations and some municipally/corporate owned transportation depots.
ElectricFish’s 350² integrated energy storage and EV charging unit is easy and fast to deploy. It works with the existing electrical grid connection and can be installed in 2-3 hours. This considerably improves existing solutions, which can take days to install, disturbing customers’ business and the surrounding environment.
Another key advantage is that our solution withdraws less power from the grid. Transformers, which step up and down the voltage at substations, do not cope well with high power withdrawal. As our solution can withdraw electricity from the grid with lower power, we can help transformers to last longer and, thus, save money. [Want to learn more about transformers and substations? Check out Survivaltech.club’s deep dive on the electric grid.]
Energy storage and fast EV charging services are highly complementary, so integrating them makes a lot of sense. Usually, the demand for EV charging is the highest during the morning and evening. In contrast, electricity is most abundant during other times and can be stored. Our proprietary data models ensure that the charging takes place at the right time.
Our energy storage system can be used in emergencies as backup power, for keeping charging operations on and providing energy to host sites.
Who are your customers and partners?
We have three customer segments: 1) convenience stores/gas station owners, 2) fleet operators, and 3) utilities.
Convenience stores, colocated generally with gasoline pumps, were our first target customers. Our fast EV chargers can provide a gasoline-like experience for the customers, where they can get their EV charged, grab something to eat, and continue their journey. Our EV chargers can deliver up to 200 miles (320 kilometers) of range to EVs in 10 minutes.
More fleet operators are planning to electrify their vehicles. They are now looking for an EV charging solution that can be quickly deployed. There is huge inbound traction with enterprise customers (e.g, fleets, dealers) struggling with quick deployment and resilience in their operations.
Electric utilities are also interested in our product as either adding energy storage at substations or providing EV charging services for their customers. We are part of several electric utilities’ innovation programs across the US.
Utilities are not only our customers but also essential partners. As our product can feed electricity back to the grid, we need to have contacts with electric utilities to participate in the real-time energy markets. For example, demand response and capacity bidding market offer an attractive potential revenue stream for our service.
The biggest testimonial for us is the investment from engineering and planning firm, Black & Veatch, that does permitting, and installation for charging stations for the likes of Tesla, Electrify America, and others.
What kind of battery chemistry does your product use? How have you built your supply chain?
Our energy storage unit uses lithium-ion batteries at the moment. More specifically, we use a lithium iron phosphate battery, as it is slightly safer in case of a fire.
I personally look forward to the development of zinc batteries. Zinc batteries are even safer than lithium-iron phosphate batteries because they can withstand higher temperatures.
In our supply chain, we are working with partners that can develop and supply whole components to our system. We have a lot of domestic supply partners, primarily in batteries.
The US Congress passed the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) in August 2022 with $374 billion on clean energy and climate resiliency. How does the IRA affect your business?
The passing of the IRA was definitely exciting for us! As far as we understand, we will get around 30% of the initial hardware deployment cost back as tax credits.
I’m looking forward to the IRA unfolding in the next few years. The IRA represents a significant change for numerous climate tech businesses in the US.
How can the Survivaltech.club readers help you?
We are looking for 2-3 new team members to join in building the future of resilient and electric communities!
We are looking for a mechanical/electrical engineer to scale our prototypes and a data scientist with experience in data engineering and optimization. We would also love to welcome a project manager to our team who could evolve into a chief of staff role later.
Most importantly, we are looking for mission-driven people that are excited about building hardware! Check out the open positions here.
I’d love to hear feedback and connect with fellow climate people! Contact me at pauliina@survivaltech.club, Twitter, or LinkedIn.
If you found this article useful, please consider sharing it with your network!🌍
➡️Follow Survivaltech.club on Twitter and Linkedin
Best, Pauliina💚








Really enjoyed reading this piece! It's interesting how the EV infrastructure is evolving in the US. Very much visible in the possible business models. Thanks for putting this together Pauliina!